Urinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults
Condition Basics
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a problem that happens when germs (called bacteria) get into the urinary tract and cause an infection.
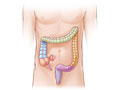
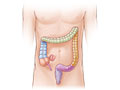
Your urinary tract, Opens dialog is the system that makes urine and carries it out of your body. It includes your bladder and kidneys and the tubes that connect them.
Most UTIs are bladder infections, Opens dialog. A bladder infection most often isn't serious if it's treated right away. But if you don't take care of a bladder infection, it can spread to your kidneys. A kidney infection, Opens dialog is serious and can cause lasting damage.
What causes it?
UTIs are caused by germs (bacteria). The germs that most often cause these infections live in your large intestine and are found in your stool. The germs usually get into your urinary tract, Opens dialog through your urethra, Opens dialog. The urethra carries urine from your bladder to the outside of your body.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of a UTI may include pain or burning when you urinate. You may have an urge to urinate often, but you will usually pass only small amounts of urine. Your urine may be cloudy, look pink or red, or smell bad. You may feel pain in your lower belly or have flank pain, Opens dialog.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor will test a sample of your urine to see if it has germs that cause infections. Your doctor will also ask you about your past health and do a physical exam. If you have infections often, you may need more tests to find out why.
How is a UTI treated?
Antibiotics can cure most UTIs. It may help to drink lots of water and other fluids. Urinate often, and empty your bladder each time. For pain and burning, your doctor may advise you to take a medicine called phenazopyridine. If the UTI affects your kidneys or causes widespread infection, you may need hospital care.
How can you prevent a UTI?
There are some things you can do that may help prevent UTIs. For example, drinking more water may help. Take time to empty your bladder as much as you can when you urinate. If you're a sexually active woman, make sure to urinate soon after you have sex.
UTIs are caused by germs (bacteria). They enter the urethra, Opens dialog and travel up the urinary tract, Opens dialog.
- Germs that normally live in the large intestine, Opens dialog and are in feces (stool) are the most common source of infection.
- Sexual intercourse may move bacteria into the urinary tract. This is more common in women.
- Catheters are a common source of infection in people who are in hospitals or long-term care centers. Catheters are flexible tubes put into the bladder to allow urine to drain.
- Sometimes bacteria traveling through the blood or lymph system, Opens dialog can cause kidney or bladder infections.
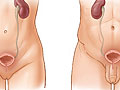
Women tend to get more bladder infections than men. This is likely because women have shorter urethras, and their rectums are closer to their urethras. So it's easier for germs to move up to the bladder.
UTIs in older men are often related to prostate problems. Having an enlarged prostate can limit the body's ability to pass urine.
Tips for women
You can take steps to prevent UTIs.
- Hydrate.
Drinking more water and other liquids may help.
Some women have found cranberry juice to be helpful, although the evidence from studies isn't strong.
- Empty completely.
When you urinate, take time to empty your bladder as much as you can.
- Prevent UTIs from sex.
Urinate immediately after sexual intercourse.
Avoid using condoms coated with spermicide or a diaphragm for birth control. If you get UTIs often, ask your doctor about taking antibiotics right after sexual intercourse to prevent recurrent UTIs.
- Clean correctly.
Your doctor may suggest that you wipe from front to back after you use the toilet. This can help you avoid spreading bacteria from your anus to your urinary tract.
Tips for men
You can take steps to prevent UTIs.
- Hydrate.
Drinking more water and other liquids may help.
- Empty completely.
When you urinate, take time to empty your bladder as much as you can.
- Keep clean.
Keep the tip of your penis clean, especially if you aren't circumcised. The foreskin can trap bacteria, which can then get into the urinary tract and cause infection.
Learn more
The symptoms are different depending on where the infection is.
Symptoms of a UTI in the bladder include:
- Pain or burning when you urinate.
- An urge to urinate often, but usually passing only small amounts of urine.
- Pain in the lower belly.
- Urine that looks cloudy, is pink or red, or smells bad.
Symptoms of a UTI in the kidneys include:
- Pain in the flank, Opens dialog. This is felt just below the rib cage and above the waist on one or both sides of the back.
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Some people have bacteria in their urinary tract without having any symptoms. It may lead to infections that cause symptoms, but in many cases it doesn't. It usually goes away without treatment.
Most UTIs clear up quickly with antibiotics. How long treatment takes and if you will need urine tests will vary. It depends on where the infection is (bladder or kidneys), how often you get one, and how serious it is. Kidney infections and UTIs that are complicated by other things will take longer to treat.
Sometimes UTI symptoms go away when you're taking antibiotics but they come back when you're done taking the medicine. This is called a relapse. It often means that the antibiotics didn't clear up the infection. Or there could be another problem affecting the urinary tract.
Call your doctor now if painful urination or other symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) occur with:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fever and chills.
- Pain in the flank, Opens dialog, which is felt just below the rib cage and above the waist on one or both sides of the back, or lower belly pain.
Call your doctor now if you are pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI (listed above).
Call a doctor if you:
- Have had UTI symptoms before and you have those symptoms again.
- Have minor symptoms of a UTI that do not clear up in 1 to 2 days, such as pain or burning when you urinate, foul-smelling urine, or the urge to urinate frequently while passing only small amounts of urine.
- Notice blood or pus in your urine.
- Have symptoms of a UTI and you have diabetes.
- Have been taking antibiotics for a UTI but your symptoms do not improve or they come back (recur) after improving temporarily.
Watchful waiting
Watchful waiting is not the right choice if you suspect that you or your child has a urinary tract infection.
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor will ask for a sample of your urine. It's tested to see if it has germs that cause bladder infections. Your doctor will also ask you about your past health and do a physical exam.
If your doctor thinks you have a UTI, he or she may have you start taking antibiotics right away. You won't have to wait for the results of your test.
Your doctor may do other tests if you have infections often, if antibiotics don't help, or if the infection comes back. You may also need more tests if the UTI causes other problems or if your kidneys are infected. You may get tests to see if there are problems with your urinary tract that make you more likely to get UTIs. Sometimes tests are needed to find out if the UTI is caused by unusual bacteria.
Learn more
Watch
Antibiotics can cure most UTIs.
- Bladder infections.
Treatment for bladder infections is usually a mix of antibiotics and home treatment. Home treatment includes drinking lots of water and fluids and urinating often.
- Kidney infections.
Antibiotics usually can treat kidney infections. But you may need a brief hospital stay and a short course of I.V. antibiotics if you're too ill or sick to your stomach to take medicine by mouth.
Your doctor may advise you to take medicine for symptoms like pain or burning. This medicine is called phenazopyridine. You can buy it without a prescription. But it doesn't treat the infection. You'll still need antibiotics. Don't use this medicine for flank pain or kidney infections.
If your UTI doesn't improve after you take antibiotics, you'll need more evaluation and more antibiotic treatment.
If you have a severe kidney infection, or if a bladder or kidney infection causes other problems, you may need hospital care.
Learn more
You can care for a UTI at home by taking action at the first sign of any pain or burning when you urinate. Try these tips:
These steps won't cure a UTI, so don't delay getting medical treatment and starting on an antibiotic if you have an infection.
- Drink lots of water.
This is especially important during the first 24 hours after your symptoms appear. This will help make the urine less concentrated and wash out the infection-causing bacteria. This may alter some of your body's normal defense mechanisms. But most doctors recommend drinking a lot of fluids when you have a UTI.
- Avoid drinks that are carbonated or have caffeine.
They can irritate your bladder.
- Urinate often and completely.
Empty your bladder each time.
- Take a hot bath or lay a heating pad over your genital area.
This helps to relieve pain.
Never go to sleep with a heating pad in place.
Learn more
Watch
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.