Top of the pageCheck Your Symptoms
Knee Problems and Injuries
Overview
Most people have had a minor knee problem at some time. Most of the time our body movements don't cause problems. But sometimes symptoms develop from everyday wear and tear, overuse, or injury. Knee problems and injuries most often occur during sports or recreational activities, work-related tasks, or home projects.
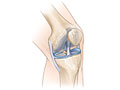
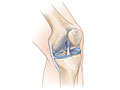
The upper and lower bones of the knee, Opens dialog are separated by two discs (menisci, Opens dialog). The upper leg bone (femur) and the lower leg bones (tibia and fibula) are connected by ligaments, Opens dialog, tendons, Opens dialog, and muscles. The surface of the bones inside the knee joint is covered by articular cartilage. It absorbs shock and provides a smooth, gliding surface for joint movement.
Knee problems are often caused by an injury to one or more of these parts of the knee. But they may be caused by things other than injuries. Some people are more likely to have knee problems than others. Many jobs, sports and activities, getting older, or having a disease such as osteoporosis, Opens dialog or arthritis increase your chances of having problems with your knees.
Sudden (acute) injuries
Injuries are the most common cause of knee problems. Sudden (acute) injuries may be caused by a direct blow to the knee. Or they may be caused by abnormal twisting, bending the knee, or falling on the knee. Pain, bruising, or swelling may be severe and occur within minutes of the injury. Nerves or blood vessels may be pinched or damaged during the injury. The knee or lower leg may feel numb, weak, or cold. It may tingle or look pale or blue. Acute injuries include:
- Sprains, Opens dialog, strains, Opens dialog, or other injuries to the ligaments and tendons that connect and support the kneecap.
- A tear in the rubbery cushions of the knee joint (meniscus, Opens dialog).
- A torn ligament, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), Opens dialog. The medial collateral ligament (MCL), Opens dialog is the most often injured ligament of the knee.
- Breaks (fracture, Opens dialog) of the kneecap, lower portion of the femur, or upper part of the tibia or fibula. Knee fractures are most often caused by abnormal force. Examples include falling on the knee, a severe twisting motion, severe force that bends the knee, and the knee forcefully hitting an object.
- Kneecap dislocation, Opens dialog. This type of injury occurs more often in active teens and young adults.
- Pieces of bone or tissue (loose bodies) from a fracture or dislocation. They may get caught in the joint and interfere with movement.
- Knee joint dislocation. This is a rare injury that requires great force. It's a serious injury. It requires medical care right away.
Overuse injuries
Overuse injuries occur with repetitive activities or repeated or prolonged pressure on the knee. Knees can get irritated and inflamed when you climb stairs, ride a bike, jog, or jump, putting stress on your joints and other tissues. Overuse injuries include:
- Inflammation of the small sacs of fluid that cushion and lubricate the knee (bursitis, Opens dialog).
- Inflammation of the tendons (tendinitis, Opens dialog) or small tears in the tendons (tendinosis).
- Thickening or folding of the knee ligaments (plica syndrome).
- Pain in the front of the knee from overuse, injury, excess weight, or problems in the kneecap (patellofemoral pain syndrome, Opens dialog).
- Irritation and inflammation of the band of fibrous tissue that runs down the outside of the thigh (iliotibial band syndrome).
Conditions that may cause knee problems
Problems not directly related to an injury or overuse may occur in or around the knee.
- Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, Opens dialog (degenerative joint disease). This may cause knee pain. It often occurs at the site of a previous injury.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease, Opens dialog. This causes pain, swelling, and tenderness in the front of the knee below the kneecap.
- A popliteal (or Baker's) cyst, Opens dialog. This causes swelling in the back of the knee.
- Infection in the skin (cellulitis, Opens dialog), joint (infectious arthritis, Opens dialog), bone (osteomyelitis, Opens dialog), or bursa, Opens dialog (septic bursitis, Opens dialog). This can cause pain and decreased knee movement.
- A problem elsewhere in the body. Things like a pinched nerve or a problem in the hip can sometimes cause knee pain.
- Osteochondritis dissecans. This causes pain and decreased movement when a piece of bone or cartilage (or both) inside the knee joint loses blood supply and dies.
Treatment
Treatment for a knee problem or injury may include first aid, rest, bracing, physical therapy, and medicine. In some cases, surgery is needed. Treatment depends on:
- The location and type of injury, and how bad it is.
- Your age, health condition, and activity level (such as work, sports, or hobbies).
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Major trauma is any event that can cause very serious injury, such as:
- A fall from more than 10 ft (3.1 m)[more than 5 ft (1.5 m) for children under 2 years and adults over 65].
- A car crash in which any vehicle involved was going more than 20 miles (32 km) per hour.
- Any event that causes severe bleeding that you cannot control.
- Any event forceful enough to badly break a large bone (like an arm bone or leg bone).
When an area turns blue, very pale, or cold, it can mean that there has been a sudden change in the blood supply to the area. This can be serious.
There are other reasons for color and temperature changes. Bruises often look blue. A limb may turn blue or pale if you leave it in one position for too long, but its normal color returns after you move it. What you are looking for is a change in how the area looks (it turns blue or pale) and feels (it becomes cold to the touch), and this change does not go away.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Pain in children 3 years and older
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the child can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain. No one can tolerate severe pain for more than a few hours.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt the child's normal activities and sleep, but the child can tolerate it for hours or days.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The child notices and may complain of the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt his or her sleep or activities.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
With severe bleeding, any of these may be true:
- Blood is pumping from the wound.
- The bleeding does not stop or slow down with pressure.
- Blood is quickly soaking through bandage after bandage.
With moderate bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding slows or stops with pressure but starts again if you remove the pressure.
- The blood may soak through a few bandages, but it is not fast or out of control.
With mild bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding stops on its own or with pressure.
- The bleeding stops or slows to an ooze or trickle after 15 minutes of pressure. It may ooze or trickle for up to 45 minutes.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may quickly occur after a sudden illness or injury.
Adults and older children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Feeling very dizzy or lightheaded, like you may pass out.
- Feeling very weak or having trouble standing.
- Not feeling alert or able to think clearly. You may be confused, restless, fearful, or unable to respond to questions.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may occur quickly after a sudden illness or injury.
Babies and young children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Being very sleepy or hard to wake up.
- Not responding when being touched or talked to.
- Breathing much faster than usual.
- Acting confused. The child may not know where he or she is.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Put direct, steady pressure on the wound until help arrives. Keep the area raised if you can.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
R 14.3.0.0
Try the following tips to help relieve knee pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Rest.
It's important to rest and protect the affected area. Stop, change, or take a break from any activity that may be causing your pain or soreness.
When you rest, place a small pillow under your knee.
- Use ice.
Put ice or a cold pack on your knee for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Try to do this every 1 to 2 hours for the next 3 days (when you are awake).
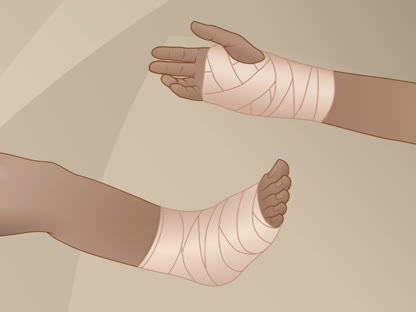
- Wrap the affected area.
Compression, or wrapping the area with an elastic bandage (such as an Ace wrap), will help reduce swelling.
- Don't wrap it too tightly, because that can cause more swelling below the affected area. Loosen the bandage if it gets too tight. Signs that the bandage is too tight include numbness, tingling, increased pain, coolness, and swelling in the area below the bandage.
- Don't expect the bandage to protect or stabilize a knee injury.
- Elevate the affected area.
Try to keep the area at or above the level of your heart to help reduce swelling. Prop up the area on pillows while you apply ice and anytime you sit or lie down.
- Try not to put weight on your knee.
Do this until you can get advice from your doctor.
- Use a cane or crutch in the hand opposite your painful knee.
- Use two crutches, keeping weight off the leg with the sore knee. You can get canes or crutches from most drugstores. Crutches are recommended if a cane causes you to walk with a limp.
- Avoid more swelling.
For 48 hours, avoid things that might increase swelling. These things include hot showers, hot tubs, hot packs, and drinks that contain alcohol.
- Apply heat.
- After 2 or 3 days, you can try applying heat to the area that hurts. Types of heat therapy include microwavable packs and disposable heating patches.
- Apply heat for 10 to 20 minutes at a time.
- You might also try switching between cold and heat.
- Rub the area.
Gently massage or rub the area to relieve pain and encourage blood flow. Don't massage the affected area if it causes pain.
- Do exercises to keep flexibility.
Try these stretches:
- Avoid high-impact exercises.
These include running, skiing, snowboarding, and playing tennis. Don't try them until your knee is no longer painful or swollen.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking slows healing because it decreases blood supply and delays tissue repair.
If you need to use a wrap for more than 48 hours, you may have a more serious injury that needs to be checked by a doctor.
Signs of possible abuse
Most injuries are not caused by abuse. But bruises are often the first sign of possible abuse. Suspect physical abuse of a child or vulnerable adult when:
- Any injury cannot be explained or does not match the explanation.
- Repeated injuries occur.
- Explanations change for how the injury happened.
You may be able to prevent further injuries by reporting abuse. Seek help if:
- You suspect child abuse or elder abuse. Call your local child or adult protective agency, police, or a health professional, such as a doctor, nurse, or counselor.
- You or someone you know is experiencing intimate partner violence (IPV).
- You have trouble controlling your anger with a child or other person in your care.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse pain or swelling.
- New signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, pus, or a fever.
- New or worse numbness, tingling, or cool and pale skin.
- Movement or strength decreases.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Watch
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Topic Contents
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.