Top of the pageCheck Your Symptoms
Mouth Problems, Noninjury
Overview
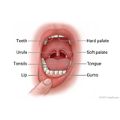
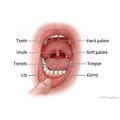
It is not unusual to have a problem with your mouth, Opens dialog from time to time. A mouth problem can involve your gums, lips, tongue, or inner cheeks, the roof of your mouth (soft and hard palates), under your tongue, your neck, or your teeth. Your mouth may be dry, or food may not taste right. You may have bad breath or a sore on your lip, gums, or tongue that makes it hard to eat or talk. Many of these problems can get better with home treatment.
Common mouth problems include:
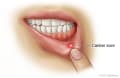
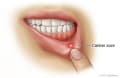
- Sores, such as cold sores, Opens dialog (also called fever blisters) and canker sores, Opens dialog. Canker sores form inside the mouth, while cold sores and impetigo usually affect the area around the outside of the mouth.
- Infections. These can be caused by a virus (such as herpes simplex, Opens dialog) or by bacteria (such as epiglottitis, Opens dialog, or impetigo, Opens dialog, or a sexually transmitted infection, Opens dialog). An infection is more serious when it causes rapid swelling of the tongue or throat and blockage of the airway.
- Tender, red splits or cracks at the corner of your mouth (angular cheilitis, Opens dialog). These can be caused by infection, a diet too low in vitamins, and over-closure of the mouth in someone who has been without teeth or dentures for some time.
- Chapped lips. They can be caused by dry, windy, cold, or very hot weather.
- Dry mouth (xerostomia). A common cause of dry mouth is dehydration, Opens dialog. Over time, having a dry mouth increases your risk of mouth infections, gum disease, and dental cavities.
- Thick, hard, white patches inside the mouth that can't be wiped off (leukoplakia). This is commonly caused by irritation of the mouth, such as from a rough tooth or poorly fitting dentures rubbing against tissue or from smoking or using smokeless (spit) tobacco.
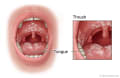
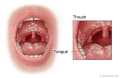
- Thrush, Opens dialog. This is a common infection of the mouth and tongue. It's caused by the yeast Candida albicans. Thrush appears on the mouth and tongue as white patches that look like cottage cheese or milk curds. When the patches are wiped away, the area underneath looks red and raw and may bleed. In babies, thrush may cause a rash in the diaper area.
- Taste changes. Your sense of taste may be decreased, lost, or changed, such as a metallic taste in your mouth.
Your tongue may become sore or swollen, or it may change color or texture. A buildup of food and bacteria on the tongue may make the tongue look thick or furry ("hairy tongue"). Often the problems will go away if the surface of the tongue is regularly brushed with a soft-bristled toothbrush. If your tongue problem is from some local irritation, such as tobacco use, the tongue problem may clear up when you remove the source of the irritation. Rapid swelling of the tongue can be caused by an allergic reaction, Opens dialog, which can interfere with breathing.
Bad breath (halitosis) or changed breath can make you feel embarrassed. Make sure that you brush your teeth twice each day and floss once a day to decrease the bacteria that can cause bad breath. Brushing your tongue can also help.
The use of alcohol and tobacco can cause many mouth problems. Your chances of having oral cancer, Opens dialog are higher if you smoke, use smokeless (chew) tobacco, or use too much alcohol.
Mouth problems may occur more often with other conditions and diseases, such as diabetes, Opens dialog, Down syndrome, Opens dialog, and HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), Opens dialog. Many medicines also can cause mouth problems.
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
You can get dehydrated when you lose a lot of fluids because of problems like vomiting or fever.
Symptoms of dehydration can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel tired and edgy (mild dehydration), or you may feel weak, not alert, and not able to think clearly (severe dehydration).
- You may pass less urine than usual (mild dehydration), or you may not be passing urine at all (severe dehydration).
Severe dehydration means:
- Your mouth and eyes may be extremely dry.
- You may pass little or no urine for 12 or more hours.
- You may not feel alert or be able to think clearly.
- You may be too weak or dizzy to stand.
- You may pass out.
Moderate dehydration means:
- You may be a lot more thirsty than usual.
- Your mouth and eyes may be drier than usual.
- You may pass little or no urine for 8 or more hours.
- You may feel dizzy when you stand or sit up.
Mild dehydration means:
- You may be more thirsty than usual.
- You may pass less urine than usual.
Severe dehydration means:
- The baby may be very sleepy and hard to wake up.
- The baby may have a very dry mouth and very dry eyes (no tears).
- The baby may have no wet diapers in 12 or more hours.
Moderate dehydration means:
- The baby may have no wet diapers in 6 hours.
- The baby may have a dry mouth and dry eyes (fewer tears than usual).
Mild dehydration means:
- The baby may pass a little less urine than usual.
Many prescription and nonprescription medicines can cause mouth problems. A few examples are:
- Antibiotics.
- Some seizure medicines.
- Medicines used to treat cancer (chemotherapy).
- Steroid medicines.
- Medicines used after organ transplant.
Symptoms of difficulty breathing can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel a little out of breath but still be able to talk (mild difficulty breathing), or you may be so out of breath that you cannot talk at all (severe difficulty breathing).
- It may be getting hard to breathe with activity (mild difficulty breathing), or you may have to work very hard to breathe even when you're at rest (severe difficulty breathing).
Severe trouble breathing means:
- You cannot talk at all.
- You have to work very hard to breathe.
- You feel like you can't get enough air.
- You do not feel alert or cannot think clearly.
Moderate trouble breathing means:
- It's hard to talk in full sentences.
- It's hard to breathe with activity.
Mild trouble breathing means:
- You feel a little out of breath but can still talk.
- It's becoming hard to breathe with activity.
Severe trouble breathing means:
- The child cannot eat or talk because he or she is breathing so hard.
- The child's nostrils are flaring and the belly is moving in and out with every breath.
- The child seems to be tiring out.
- The child seems very sleepy or confused.
Moderate trouble breathing means:
- The child is breathing a lot faster than usual.
- The child has to take breaks from eating or talking to breathe.
- The nostrils flare or the belly moves in and out at times when the child breathes.
Mild trouble breathing means:
- The child is breathing a little faster than usual.
- The child seems a little out of breath but can still eat or talk.
Symptoms of a stroke may include:
- Sudden numbness, tingling, weakness, or paralysis in your face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of your body.
- Sudden vision changes.
- Sudden trouble speaking.
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding simple statements.
- Sudden problems with walking or balance.
- A sudden, severe headache that is different from past headaches.
Babies can quickly get dehydrated when they lose fluids because of problems like vomiting or fever.
Symptoms of dehydration can range from mild to severe. For example:
- The baby may be fussy or cranky (mild dehydration), or the baby may be very sleepy and hard to wake up (severe dehydration).
- The baby may have a little less urine than usual (mild dehydration), or the baby may not be urinating at all (severe dehydration).
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
To do home treatment for a black or coated tongue:
- Brush your tongue daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and toothpaste or a solution of 1 part hydrogen peroxide to 2 parts water.
- Scrape the tongue with the edge of a spoon to remove the furry coating.
- Do not use tobacco.
Bismuth products, such as Pepto-Bismol, can turn your tongue black. The black color will go away after you stop taking the medicine.
Sudden drooling and trouble swallowing can be signs of a serious problem called epiglottitis. This problem can happen at any age.
The epiglottis is a flap of tissue at the back of the throat that you can't see when you look in the mouth. When you swallow, it closes to keep food and fluids out of the tube (trachea) that leads to the lungs. If the epiglottis becomes inflamed or infected, it can swell and quickly block the airway. This makes it very hard to breathe.
The symptoms start suddenly. A person with epiglottitis is likely to seem very sick, have a fever, drool, and have trouble breathing, swallowing, and making sounds. In the case of a child, you may notice the child trying to sit up and lean forward with his or her jaw forward, because it's easier to breathe in this position.
Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) may include:
- The sudden appearance of raised, red areas (hives) all over the body.
- Rapid swelling of the throat, mouth, or tongue.
- Trouble breathing.
- Passing out (losing consciousness). Or you may feel very lightheaded or suddenly feel weak, confused, or restless.
- Severe belly pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
A severe reaction can be life-threatening. If you have had a bad allergic reaction to a substance before and are exposed to it again, treat any symptoms as an emergency. Even if the symptoms are mild at first, they may quickly become very severe.
Symptoms of a heart attack may include:
- Chest pain or pressure, or a strange feeling in the chest.
- Sweating.
- Shortness of breath.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Pain, pressure, or a strange feeling in the back, neck, jaw, or upper belly, or in one or both shoulders or arms.
- Lightheadedness or sudden weakness.
- A fast or irregular heartbeat.
For men and women, the most common symptom is chest pain or pressure. But women are somewhat more likely than men to have other symptoms like shortness of breath, tiredness, nausea, and back or jaw pain.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in children are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and congenital heart disease.
- Steroid medicines, which are used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Not having a spleen.
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your dentist or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your dentist or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your dentist in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your dentist or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
After you call 911, the operator may tell you to chew 1 adult-strength (325 mg) or 2 to 4 low-dose (81 mg) aspirin. Wait for an ambulance. Do not try to drive yourself.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
R 14.3.0.0
Caring for a sore or ulcer inside your mouth
Try these tips to help care for a sore or ulcer inside your mouth.
- Make changes in your diet to relieve pain when you eat or drink.
- Drink cold drinks, such as water or iced tea, or eat flavored ice pops or frozen juices. Use a straw to keep the liquid from touching your mouth sore.
- Eat soft, bland foods that are easy to swallow. These include ice cream, custard, applesauce, cottage cheese, macaroni and cheese, soft-cooked eggs, yogurt, and cream soups.
- Cut foods into small pieces. Or you can grind, mash, blend, or puree foods.
- Avoid coffee, chocolate, spicy and salty foods, citrus fruits, nuts, seeds, and tomatoes.
- Avoid very hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks if they make your pain worse.
Lip care
Try these tips to help treat chapped lips.
- Avoid licking or biting your lips.
- Avoid sun or wind exposure, and use a lip balm with sunscreen.
- For severely chapped lips, build a barrier by applying petroleum jelly, such as Vaseline.
- Use a humidifier in your home. Follow the directions for cleaning the machine.
Treating a bad taste
Everyone gets a bad taste in the mouth from time to time. Try the following simple home treatment measures to improve the taste in your mouth.
- Gargle with water.
- Using toothpaste, brush your teeth, tongue, roof of your mouth, and gums at least two times a day.
- Rinse your mouth with mouthwash.
- Drink liquids, chew sugar-free gum or mints, or suck on sour candies.
- Use plastic utensils if you have a bitter or metallic taste when eating.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or a fever.
- New or worse dehydration, Opens dialog.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.